- Created by BrianQ, last modified by StevenR on Feb 10, 2017
You are viewing an old version of this page. View the current version.
Compare with Current View Page History
« Previous Version 21 Next »
https://help.myob.com/wiki/x/jqsHAQ
How satisfied are you with our online help?*
Just these help pages, not phone support or the product itself
Why did you give this rating?
Anything else you want to tell us about the help?
Australia only. For New Zealand, see Setting up GST codes (New Zealand)
Tax codes are used to track tax paid to and by your business. Each code represents a particular type of tax.
AccountRight has an extensive list of codes that can be used in a variety of situations—for example, when doing business with overseas customers, when tracking capital acquisitions, and so on.
Summary of tax types
When you create a tax code, you need to select which type of tax it is. The table below describes what each tax type is for.
| Tax Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Consolidated | This tax type is used for taxes that are made up of two or more tax codes or sub-taxes. |
| Import Duty | Importers, who are bringing goods into Australia from other countries, should use this tax type. Tax codes with this tax type are used to record the import duty payable on a purchase order without changing the total amount of the purchase order. (The import duty is treated as a separate transaction since the duty is payable to the ATO, not to the company supplying the goods.) |
| Sales Tax | This tax type is associated with the Wine Equalisation Tax. |
| Goods & Services Tax | This tax type is associated with the Goods & Services Tax assigned to sales and purchases. This tax type also is used for GST-free goods and GST on Wine Equalisation Tax. |
| Input Taxed | This tax type should be used by organisations, such as suppliers of financial services, that must pay GST on the purchases they make but don't collect GST from their clients or customers. The Input Taxed tax type also should be used by businesses that haven't registered for GST. |
| Luxury Car Tax | This tax type is used by the Automotive industry to handle the luxury car tax. |
| Voluntary withholdings | This tax type should be used for the PAYG voluntary withholdings scheme. |
| No ABN/TFN | This tax type should be used for suppliers that have not quoted ABNs on their invoices, or for amounts that are withheld from investment income because no tax file number was quoted. This type indicates that the tax code is a PAYG Withholding tax type and will always be rounded down to the nearest dollar. You should use a No ABN/TFN tax code of 49% for suppliers who do not quote an ABN on invoices for more than $75 tax exclusive, or where amounts are withheld from investment income because no tax file number was quoted. If both of these situations apply to your company, you will need to create two tax codes to handle them separately. |
Summary of tax codes
| Tax Code | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| GST | Goods & Services Tax | General tax of 10% on most goods, services, and other items sold or consumed in Australia |
| FRE | GST-Free | Sales that are GST-free sales other than export sales, such as fresh food purchases, medical services and products, and educational courses |
| EXP | Export Sales | Used when exporting goods, which are usually GST-Free |
| IMP | Import Sales | Denotes indirect costs of importing such as customs duty and handling costs |
| CAP | Capital Purchase | Amounts paid for capital assets, such as plant and equipment, motor vehicles, land and buildings |
| INP | Input Taxed Purchases | Used for the purchase of input taxed supplies, or supplies on which no GST is added to the final purchase price, such as residential rents or unit trusts |
| ITS | Input Taxed Sales | Used for the sale of input taxed supplies, or supplies that don't include GST in the sale price, such as financial supplies, interest income and residential income |
| LCT | Luxury Car Tax | Used to handle special tax considerations which accompany the sale of luxury cars |
| GNR | GST Not Registered | Used to record purchases from suppliers who have an ABN but are not registered to collect GST |
| ABN | No ABN Withholding | Used for suppliers that have not quoted ABNs on their invoices, or for amounts that are withheld from investment income because no tax file number was quoted |
| PRI | Private Use | Adjusts the private usage portion of business expenses |
| N-T | No-Tax | Used to record sales that carry no GST, such as depreciation and cash transfers. |
| WET | Wine Equalisation Tax | Tax on wine consumed in Australia based on the value of the wine |
| GW | Consolidated Tax | Combines the Wine Equalisation GST (WEG) and Wine Equalisation Tax codes |
| VWH | Voluntary Withholdings | Used for contractor payments where a voluntary agreement is in place. |
To create a tax code
- Go to the Lists menu and choose Tax Codes. The Tax Code List window appears.
- Click New. The Tax Code Information window appears.
- In the Tax Code field, type a code (up to three characters) for the new tax and press Tab.
Complete the other fields in this window.
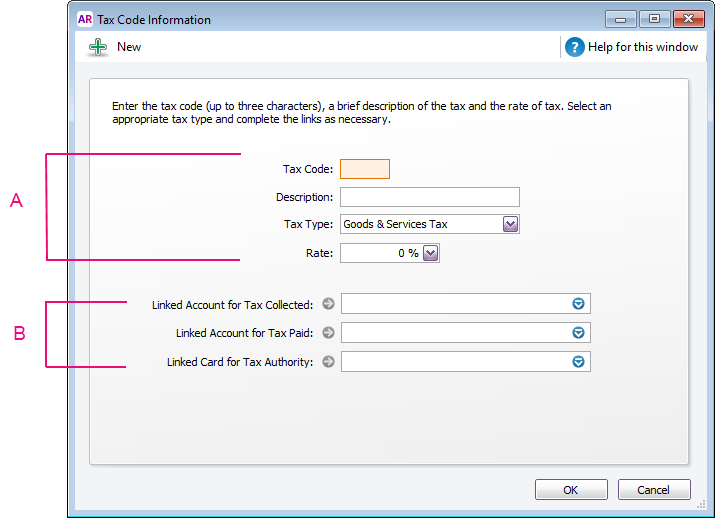
A Enter a description, type and rate. If you selected Consolidated as the Tax Type, see Consolidated tax codes. B Select the linked account for tax collected and for tax paid. These fields are only available for some tax types.
To delete a tax code
A tax code can only be deleted if it hasn't been assigned to a transaction.
To delete a tax code:
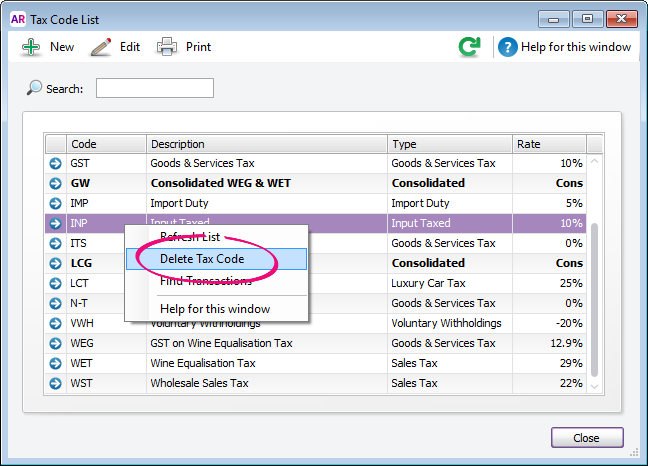
- Go to the Lists menu and choose Tax Codes. The Tax Code List window appears.
- Right-click the tax code to be deleted and choose Delete Tax Code.
Consolidated tax codes
You can create consolidated tax codes by combining two or more tax codes. For example, you could create a GW tax code (with a 41.9% tax rate) that is composed of WET (Wine Equalisation Tax) at 29% and WEG (GST on Wine Equalisation Tax) at 12.9%.
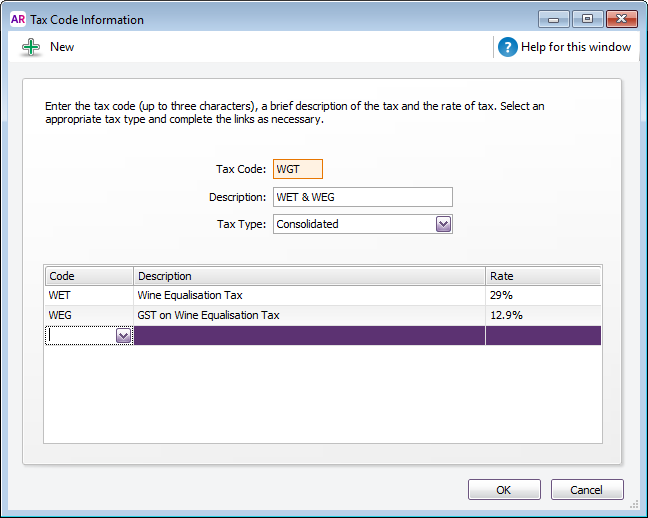
Make sure you first create the tax codes you want to consolidate. The rest of the fields are filled in for you and the consolidated tax rate is calculated automatically.
To assign tax codes to accounts
You can assign a tax code to any detail account in your accounts list. The tax code you assign will appear as the default tax code when you post a transaction to this account.
For example, you have assigned the GST tax code to your electricity expense account. When you settle your electricity bill in the Spend Money window and allocate it to this account, the GST tax code will appear in this window by default.
You can allocate a tax code to an account in the Account Information window. To open this window, go to the Accounts command centre, click Accounts List, double-click the required account, and click the Details tab.
To assign tax codes to items
When you set up an item, you must assign a GST code to use when selling it. If you use AccountRight Standard, Plus or Premier, you’ll also need to assign a GST code to use when buying the item.
These item GST codes will appear by default when buying and selling your items unless you have specified that the customer or supplier GST code is to be used instead (see below).
You assign GST codes to items in the following tabs of the Item Information window:
- Buying and Selling tabs (Not Basics)
- Profile tab (Basics).
For more information, see Creating items.
To assign tax codes to cards
You can define a default tax code for a customer or supplier (Not Basics). You would only need to select a default tax code if the customer’s or supplier’s tax status takes precedence over that of the item or service being sold or purchased.
For example, if a customer is one to whom you only ever make export sales, you should assign the EXP (Export Sales) tax code to that customer’s card.
When you create a quote, order or invoice, the tax code assigned to the customer will be used as the default. This tax code will override the item’s tax code in an item sale, and the allocation account’s tax code in a non-item sale.
Tax codes are assigned to customers in the Selling Details tab of their Card Information window.
Make sure you select the Use Customer’s Tax Code option. (If this is not selected, the customer’s tax code will not be used, even if one has been assigned.)

Similarly, in AccountRight Standard, Plus and Premier, when you create a quote, order or bill, the tax code assigned to the supplier will be used as the default. This tax code will override the item’s tax code in an item purchase and the allocation account’s tax code in a non-item purchase. Tax codes are assigned to suppliers in the Buying Details tab of their Card Information window.
Make sure you select the Use Supplier’s Tax Code option. (If this option is not selected, the supplier’s tax code will not be used, even if one has been assigned.)

Payroll tax reporting (Australia only)
Lodge your activity statement (BAS or IAS) (Australia only)

 Yes
Yes
 No
No
 Thanks for your feedback.
Thanks for your feedback.