You are viewing an old version of this page. View the current version.
Compare with Current View Page History
« Previous Version 6 Next »
https://help.myob.com/wiki/x/44UWAw
How satisfied are you with our online help?*
Just these help pages, not phone support or the product itself
Why did you give this rating?
Anything else you want to tell us about the help?
When importing goods from overseas, GST is levied at 15% of the landed cost of the goods and is payable to the customs agent, not your overseas supplier. The GST paid to customs needs to appear in Box 13 of the GST return, so you need to create one bill to record the overseas purchase and another bill to record the costs associated with the import.
The customs agent usually handles the costs associated with the import. Generally, the customs agent will arrange payment for, and collection of, the goods on arrival in New Zealand, and may pay your customs duty, freight, insurance and GST liability. You will need to reimburse the customs agent for these costs.
The way you record overseas purchases varies depending on your GST reporting basis (Payments or Invoice). Your accounting advisor will be able to provide additional information regarding anything that might be different for your business.
If you're using the Payments basis
Setting up
To track your overseas purchases and ensure the GST is reported correctly, you'll need to set up the following:
- Create two liability accounts (Accounting menu > Chart of accounts > Liabilities tab > Create account). Need a refresher on creating accounts?
- GST Input Tax Adjustments - this account might already exist in your company file
- GST Paid to Customs - this account will hold the value of GST paid to customs
Here are our example accounts as they appear in the chart of accounts:
 When preparing your GST return, link the GST Input Tax Adjustments account to Box 13 on your GST return.
When preparing your GST return, link the GST Input Tax Adjustments account to Box 13 on your GST return. - Create an Expense account (or Cost of Sales account f or the Customs Agent's charges.
Here is our example account as it appears in the chart of accounts:
Recording the overseas purchase
Depending on how you want to treat the imports costs, there are two ways you can record the overseas purchase and account for the GST.
Treat the import costs as expense items
Create a bill for the purchased goods (Purchases menu > Create bill). Need a refresher on creating bills?
Exclude the GST by selecting the GST exclusive option.
Code the purchase using the E GST code.
- If the supplier has charged you freight costs, include this on this bill.
Here's our example:

- Create a separate bill for the import costs paid to the customs agent.
- For the customs charges, allocate it to the Customs Agent Charges expense account created earlier, and use the E GST code to exclude any GST.
- For the GST on the import, allocate it to the GST Paid to Customs liability account and use the E GST code. Enter “GST on import” as the line description to make it easy to identify in your GST report.
For the import duty charged by the customs agent, allocate it to the Customs Agent Charges expense account and use the S15 GST code.
For any other expenses the customs agent may be charging you, for example overseas freight and/or insurance, allocate it to the applicable expense account and use the E GST code.
If any local freight has been charged, allocate this to the applicable freight account and use the S15 GST code.
Here's our example:
This transaction will increase expenses and record the GST to be included in the GST adjustment.
- Pay these bills as usual (Purchases menu > Create bill payment). Need a refresher for paying bills?
Transferring the GST
Before running your GST return, you need to determine the GST value from the import, then transfer this amount to the GST Input Tax Adjustments account.
Providing you've been clearly notating the line description with "GST on import" for bills, the GST value from imports will be easy to identify.
Here's how:
- Run the GST Report (Reports > Standard > GST Report).
- Filter the report for the E GST code for the relevant period.
- Sort the report by Account number.

- Record a journal entry (Accounting menu > Create general journal) to transfer the balance from the GST Paid to Customs account to the GST Input Tax Adjustment account. Need a refresher for recording journal entries?
Here's our example:
- Prepare your GST return as usual. Need a refresher?
Here's our example showing Box 13 with the applicable GST amount: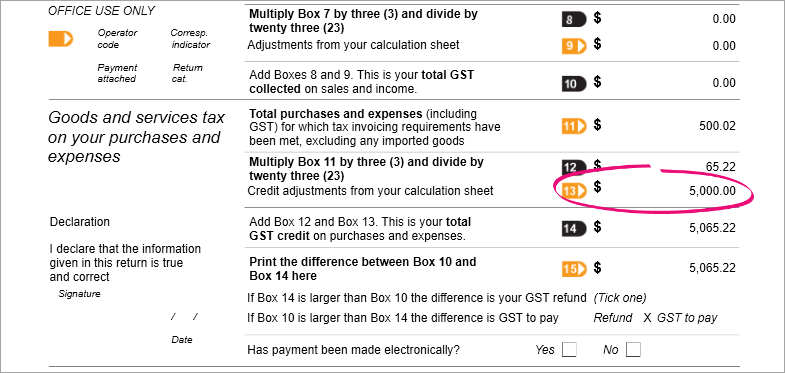
Include all costs in the purchased item's value
- Create an inventory item to track the GST on imports (Purchases menu > Items > Create item). Need a refresher for creating items?
- Name the item gstcustoms (or similar).
- Enter an Item ID (a unique alphanumeric code to identify the item). If you don't use codes to identify your inventory items, enter any number.
- Select the option I buy this item.
- For the Account for tracking purchases, choose the GST Paid to Customs liability account created earlier.
- For the Buying price ($) enter 0.00.
- The GST code should default to N-T. This is fine.
Here's our example:
Create a bill for the purchased goods, excluding any GST (Purchases menu > Create bill). Need a refresher on creating bills?
Here's our example:
If the supplier has charged you freight costs, this should be included on this bill.
- Create a separate bill for the import costs paid to the customs agent.
Click Field layout and choose Services and items.
Enter a line for the gstcustoms item created earlier, and enter its price as the GST paid to customs and use the N-T GST code.
If any local freight has been charged, allocate this to the applicable freight account and use the S15 GST code.
Here's our example:

Pay these bills as usual (Purchases menu > Create bill payment). Need a refresher for paying bills?
Transferring the GST
Before running your GST return, you need to transfer the GST amount to the GST Input Tax Adjustments account. This will increase the average cost of the item(s) and ensure the GST is reported at Box 13 of your GST return.
Here's how:
Record a journal entry (Accounting menu > Create general journal) to transfer the balance from the GST Paid to Customs account to the GST Input Tax Adjustment account. Need a refresher for recording journal entries?
Here's our example:
- Prepare your GST return as usual. Need a refresher?
Here's our example showing Box 13 with the applicable GST amount: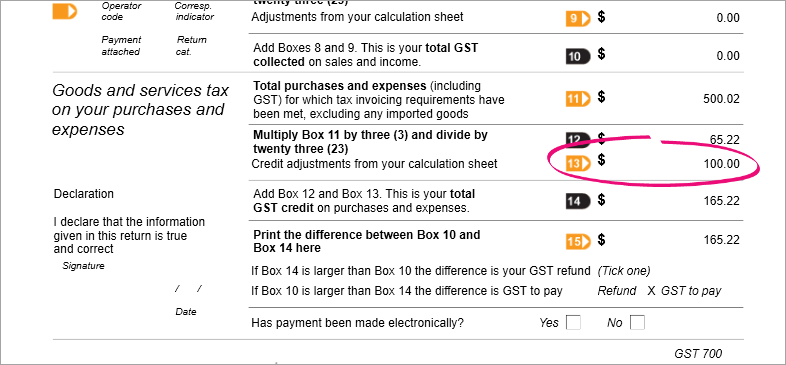
If you're using the Invoice basis
Setting up
To track your overseas purchases and ensure the GST is reported correctly, you'll need a liability account to hold the GST paid by you to the customs agent. This account will need to be linked to Box 13 on your GST return.
Check your accounts list for a liability account called GST Input Tax Adjustments (go to Accounting menu > Chart of accounts > Liabilities tab). If the account doesn't exist, click Create account to create it. Need a refresher for creating accounts?
Here is our example account as it appears in the chart of accounts: When preparing your GST return, link the GST Input Tax Adjustments account to Box 13 on your GST return.
When preparing your GST return, link the GST Input Tax Adjustments account to Box 13 on your GST return.- Create an Expense account (or Cost of Sales account) for the Customs Agent's charges.
Here's our example:
Recording the overseas purchase
Depending on how you want to treat the imports costs, there's two ways you can record the overseas purchase and account for the GST.
Create a bill for the purchased goods (Purchases menu > Create bill). Need a refresher on creating bills?
Include the GST by selecting the GST inclusive option.
Code the purchase using the E GST code.
- If the supplier has charged you freight costs, include this on this bill.
Here's our example:

- Create a separate bill for the import costs paid to the customs agent.
- For the customs charges, allocate it to the Customs Agent Charges expense account created earlier, and use the E GST code to exclude any GST.
- For the GST on the import, allocate it to the GST Paid to Customs liability account and use the E GST code. Enter “GST on import” as the line description to make it easy to identify in your GST report.
For the import duty charged by the customs agent, allocate it to the Customs Agent Charges expense account and use the S15 GST code.
For any other expenses the customs agent may be charging you, for example overseas freight and/or insurance, allocate it to the applicable expense account and use the E GST code.
If any local freight has been charged, allocate this to the applicable freight account and use the S15 GST code.
Here's our example:
Pay these bills as usual (Purchases menu > Create bill payment). Need a refresher for paying bills?
This will increase expenses and include the GST in Box 13 of your GST return.


 Yes
Yes
 No
No
 Thanks for your feedback.
Thanks for your feedback.